| A
|
| AIP genes encode a tumor suppressor protein.
Pathogenic inherited AIP mutations
are associated with Familial Isolated Pituitary Adenomas.
|
| AKT1 genes contain instructions for making a protein called AKT1 kinase, which helps control cell division and growth. It also helps control the self-destruction, or apoptosis, of cells that are not functioning properly or are no longer needed.
AKT1 genetic variants can increase susceptibility to thyroid cancer
|
| APC gene provides the genetic instructions for making APC protein, a tumor suppressor.
Pathogenic germline
APC mutations may increase the risk for colorectal
(colon) cancer, intestinal cancer, and other cancers. Familial Adenomatous
Polyposis (FAP) can also be caused by
an inherited
mutation in an APC gene.
|
| Apoptosis is
the process of programmed cell death, which is the self-destruction of cells that are not functioning properly or are no longer needed.
In cancer, apoptosis did not happen. This resulted in malignant cells
surviving and growing uncontrollably.
|
| ATM is a
tumor suppressor gene.
It helps repair damaged DNA. Inherited pathogenic mutations in this gene are associated with lymphoma, leukemia, stomach cancer, brain cancer, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, skin cancer, liver cancer, and others.
|
| ATRIP
or the ATR Interacting Protein gene, encodes protein important in DNA repair. Germline mutations in
the ATRIP gene can increase the risk of breast cancer.
|
| AXIN2
is a protein coding gene.
Pathogenic germline mutations are associated with colorectal (colon) cancer.
|
| B
|
| BAP1 gene
provides instructions for making BRCA1-Associated Protein1, which helps control cell growth, repair, and cell death.
Inherited pathogenic
mutations in this gene are associate with BAP1 Tumor Predisposition
Syndrome and an increased risk of melanoma, mesothelioma, and other cancers.
|
| BARD1 gene works in
conjunction with the BRCA1 gene to repair damaged DNA and also
as a tumor suppressor gene. Pathogenic BARD1
germline
mutations are associated with an increased risk of neuroblastoma, lung, breast, and cervical cancers.
|
| Biomarker Testing
is a laboratory test that looks for proteins, genes, and other substances found in body fluid and tissue that may be an indication of cancer or another condition. It can also used to predict a person’s risk of developing cancer or other diseases in the future. If cancer has already been diagnosed, biomarker testing can also be used to figure out the most effective treatment or to determine how well treatment is working.
|
| BMPR1A gene makes a protein that regulates cell growth and division.
Pathogenic germline
mutations in this gene are associated with Juvenile Polyposis
Syndrome and an increased risk of colorectal (colon), stomach, and intestinal cancer.
|
| BRCA
stands
for BReast
CAncer gene. Everybody has
BRCA1 & BRCA2 tumor suppressor
genes. BRCA genes produce proteins that help repair damaged DNA and prevent
cancer. Inherited pathogenic
mutations in these genes are linked to an increased risk of
various types of cancer, including breast cancer (men and women),
ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, melanoma, pancreatic cancer,
and other
cancers. Also see HBOC-- Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome.
|
| BRIP1 or BRCA1 Interacting Protein 1, works with BRCA1 to repair DNA.
Pathogenic germline
mutations in a BRIP1
gene may increase the risk for ovarian cancer and breast cancer.
|
| C
|
| Cascade Testing
is one of the most important steps in breaking the cycle of hereditary cancer in families. This testing-sharing-testing-sharing of genetic information plays a vital role in protecting the health and lives of loved ones in families with a history of cancer.
Cascade
testing requires
two
very important steps:
1. Having testing done.
2. Sharing information.
That includes sharing test results and the specific mutation in the gene, like
5385delAG in BRCA1.
The information should be shared with all these living genetic relatives: parents, siblings, aunts, uncles, nieces, nephews, and cousins.
And it needs to be shared as soon as the information is known.
(More helpful tools for sharing info with family here.)
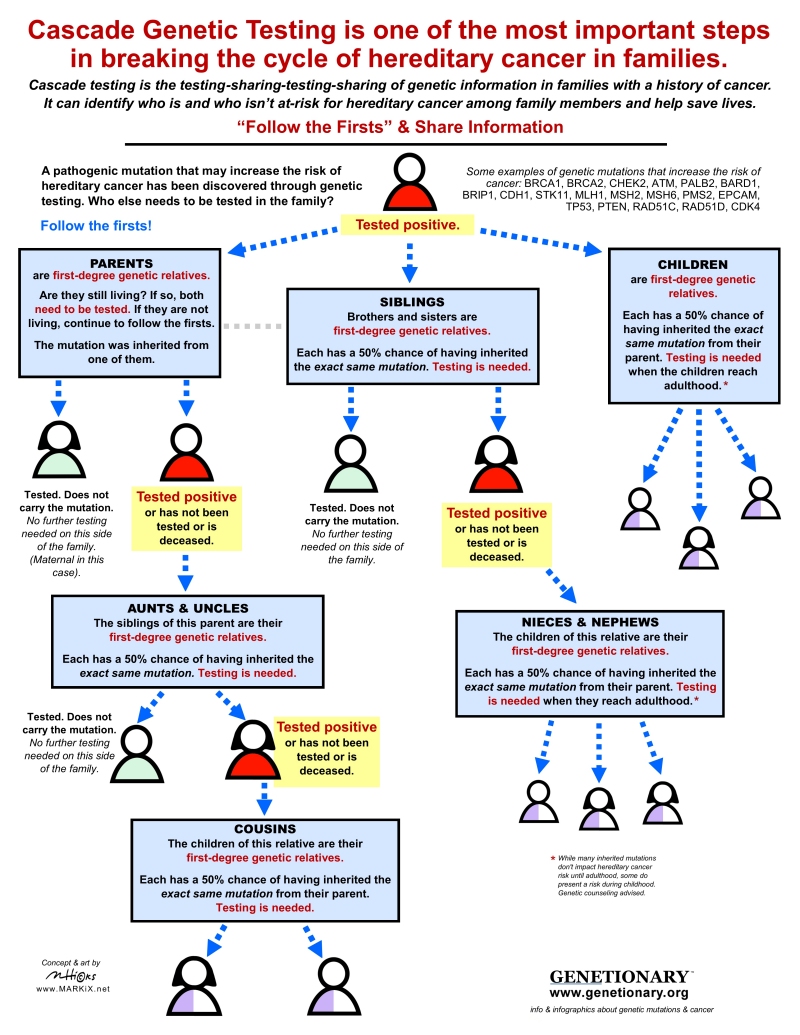
Cascade
Genetic Testing PDF
|
| CDC73 gene carries the instructions for producing a protein called parafibromin, a tumor
suppressor. Pathogenic
germline
mutations in CDC73 are associated with renal and endocrine cancers.
|
| CDH1 gene is involved in making epithelial cadherin protein. A
pathogenic
germline mutation in a CDH1 gene is associated with Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer
syndrome
(HDGC)
which increases the risk of gastric, breast, colorectal, ovarian, and thyroid cancers.
|
| CDK4 gene is a tumor suppressor gene. A
pathogenic germline CDK4 mutation is associated with an increased risk hereditary melanoma and other cancers.
|
| CDKN2A genes furnish instructions for making several proteins which act as tumor suppressors. A pathogenic germline mutation in a CDKN2A gene can increase the risk of for melanoma, pancreatic cancer, and other cancers.
|
| CDKN1B gene carries the instructions for producing p27 protein, a tumor suppressor protein involved in cell growth and division.
Pathogenic
germline in CDKN1B are associated with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 4 (MEN4) pituitary, parathyroid, and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
|
| CHEK2 (CHEckpoint
Kinase 2) is protein-coding gene. It is another tumor suppressor gene that helps with DNA repair.
Pathogenic germline mutations in this gene is linked to various types of cancer, including breast, ovarian, prostate, colon, and others.
|
| Cowden Syndrome is a hard-to-recognize condition characterized by benign overgrowths called
hamartomas. There is an increased lifetime risk of breast, thyroid, and other cancers.
Pathogenic
germline
mutations in PTEN, AKT1, and PIK3CA genes have been linked to the syndrome.
|
| CTNNA1 germline mutations are associated with gastric cancer.
(Also see CDH1 and Hereditary Diffuse Gastric
Cancer.)
|
|
D
|
|
DDX41is a protein coding gene.
Pathogenic germline mutations in DDX41 genes are associated blood cancers, specifically, familial myelodysplastic syndromes (MDSs) and acute myeloid leukemias (AMLs).
|
|
De Novo Mutations are
DNA changes that were not inherited. De novo mutations can occur
at conception, during embryonic or fetal development, after birth, or later in life.
|
|
DICER1 is RNA process regulating gene. Pathogenic germline mutations in this gene are associated with breast, ovarian, lung, brain, and other cancers.
|
| DNA or
Deoxyribonucleic acid, is the material that holds genetic instructions for the development,
functioning, and hereditary traits of every living organism on the planet. Four smaller molecules called nucleotides make up all DNA at the basic level. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA. These building blocks are composed of three parts: phosphate, sugar, and one of four types of nitrogen bases:
adenine (often denoted as "A"),
cytosine ("C"),
guanine ("G"), and
thymine ("T").
Also see RNA. |
| E
|
| EGFR gene carries the instructions for making Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) protein. EGFR is a protein that helps cells grow.
Pathogenic
germline
mutations in the EGFR gene are linked to a predisposition to lung cancer and other conditions.
|
| EPCAM is a protein coding gene.
Pathogenic
germline mutations can increase the risk of Lynch
syndrome. Which includes many cancers, but particularly colon and
rectal cancer and uterine cancer.
|
| F |
Family Health/Cancer History Pedigree Knowing your family's health history, especially if there is any history of cancer, is very important.
Download
the Family Health/Cancer History Pedigree PDF to fill out to take to your doctor and/or genetic counselor.
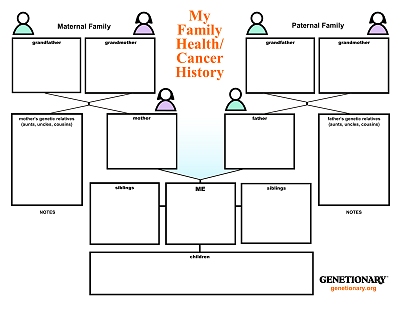
|
|
Download the
Fillable Pedigree PDF
|
| FH
(Fumarate Hydratase) is a tumor suppressor gene.
Pathogenic
germline
mutations in this gene are linked to uterine fibroids, renal/urinary
track cancer and endocrine cancer. |
| Follow
the Firsts is a concept in
cascade testing for germline mutations
that no matter who is being tested, there is always another first-degree relative that might need to be tested as well.
Download
the infographic. |
| G
|
| GALNT12
is a protein-coding gene. Pathogenic germline mutations
in GALNT12 genes are associated with an increased for colorectal cancer.
|
| Gastric Adenocarcinoma and Proximal Polyposis of the Stomach
(GAPPS)
GAPPS can cause polyps to form on the inside lining of the stomach. Polyps can be benign, but can turn cancerous spread to other parts of the body.
(More
GAPPS info from the National Institute of Health.)
|
Germline
Mutation -- Germline mutations are genetic changes that are present in genes in sperm or eggs (germ cells) at the time of conception. Some germline mutations in tumor suppressor genes can increase the risk for developing hereditary cancer. Genetic testing looks for changes in tumor suppression genes that have been linked to hereditary cancer. These particular inherited genetic
changes are called pathogenic germline mutations.
|
| H
|
| Hamartomas
are usually slow-growing noncancerous tumors. However, hamartomas may increase the risk of certain cancers. Hamartomas can grow almost anywhere on the body, but are typically found in the lungs, breast, and colon. Hamartomas are usually caused by an inherited genetic mutation.
|
| HBOC stands for
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome. It is an inherited
syndrome that increases the
risk for breast, ovarian, and other cancers. HBOC is caused by
inherited pathogenic mutations passed down in families. BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations are the most common ones associated with HBOC. PALB2, ATM and CHEK2 are some of the other mutations also associated with
HBOC.
|
| Hereditary Cancer
Week is a yearly event that begins on the last Sunday in September, with National
Previvor Day being celebrated on the Wednesday of
that week. In 2010, Congress unanimously passed a resolution creating National Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Week and National Previvor
Day. Since then, the week has been renamed National Hereditary Cancer Week
to encompass all the hereditary cancers.
|
Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer
(HDGC) is a rare cancer syndrome with an increased risk of developing two types of cancer: diffuse gastric cancer (DGC) and lobular breast cancer (LBC).
It is also associated with an increased the risk of ovarian and thyroid cancers.
(More
HDGC info from the National Institute of Health.)
|
| I |
Inherited Mutations
(see germline
mutations)
|
| J |
| K |
| KIT
is a protein coding gene.
Pathogenic germline mutations are associated with rare Familial Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST). |
|
L
|
|
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome is a rare inherited condition that increases the risk of breast cancer, osteosarcoma, gliomas and leukemia.
Pathogenic germline mutations in the
TP53
gene are associated with this disorder.
|
|
Lynch Syndrome is an inherited genetic condition associated with an increased risk of colorectal (colon) cancer, endometrial, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, and other cancers. MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, and EPCAM
pathogenic germline
mutations are all linked to the risk of Lynch Syndrome.
|
| M |
| MEN1 or Multiple
Endocrine Neoplasia type 1, is a tumor suppressor gene. Pathogenic germline mutations
in MEN1 genes are associated with pituitary, parathyroid, and enteropancreatic tumors. |
| Missense Mutation is a DNA copying mistake in which a nucleotide base pair of a gene is changed, such as thymine (T) is swapped for adenine (A).
|
| MLH1,
MSH2, MSH6, inherited
pathogenic
mutations
in these genes can increase the risk of Lynch
syndrome. Which includes many cancers, but particularly colon and
rectal cancer.
|
| Mutation --
In genetics, a mutation is a DNA sequence
change that was caused by deleting, adding, or replacing parts of your DNA.
Genetic mutations can be
somatic or germline. And
they can be either benign (causing no harm) or pathogenic
(increased risk of disease.) |
| MUTYH gene is a DNA repair gene. A
pathogenic germline
mutation in this gene can increase the risk of colorectal (colon) cancer, thyroid cancer, ovarian cancer, and other cancers. |
| N
|
| Neoplasms are abnormal growth of cells in the body. They can be cancerous or benign (non-cancerous).
|
| NF1
and NF2 genes carries the genetic instructions for producing neurofibromin protein, a tumor suppressor.
Pathogenic germline
mutations is
these genes are associated with brain cancer, breast cancer, endocrine cancer, nervous system cancer,
and gastric cancer.
|
| Nonsense Mutation is
a change in nucleotide base pair in a gene that prematurely stops the building of proteins needed for proper gene expression and function.
|
| Nucleotides
are organic compounds that the form the basic building blocks of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA. The four nucleobases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). In RNA, the base uracil (U) takes the place of thymine.
Nucleotides in genes are connected in a specific order to convey hereditary information.
|
| O |
| Oncogenes are genes that control cell growth and division that have mutated. Oncogenes have the potential to cause cancer by causing loss of function or uncontrolled cell growth.
|
| P
|
| PALB2
genes work with BRCA2 genes in DNA damage repair.
Pathogenic germline
mutations in PALB2 genes increases the risk for breast cancer,
pancreatic cancer, and ovarian cancer.
|
| Pathogenic Variant
(mutation)
is a change in a gene that increases
the risk of diseases like cancer.
|
| Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
(PJS) is an inherited cancer syndrome involving mutations in the
STK11 gene. PJS is a hereditary cancer syndrome characterized by gastrointestinal polyps and dark spots in the body and an increased cancer risk.
|
| PMS2
is one of the genes known as a mismatch repair
(MMR) genes. A pathogenic
germline mutation in a PMS2 gene is a cause of Lynch
syndrome. This mutation increases the risk for colorectal (colon) cancer, uterine (endometrial) cancer, and other cancers.
|
|
PTEN
is a tumor suppressor gene. Pathogenic
germline
mutations in this gene are linked to
Cowden Syndrome which increases your risk to breast cancer, uterine (endometrial) cancer, thyroid cancer, colorectal (colon and rectal) cancer, kidney cancer.
|
|
Previvor
is someone who has not been diagnosed with cancer but is at a higher risk for cancer due to certain
inherited genetic mutations
in tumor suppressor genes (BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, ATM, PALB2, PTEN, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, etc.) or family history.
Being a previvor does not mean you will get cancer. But a previvor needs to be proactive and monitored appropriately to reduce the risk. Many hereditary cancers can be detected early and successfully treated, or even avoided all together with preventative action.

Download
the PDF
|
| Q |
| QDPR (Quinoid Dihydropteridine Reductase) is a protein coding
gene responsible for producing the enzyme Quinoid
Dihydropteridine Reductase. Mutations in this gene can cause tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency, which affects levels of neurotransmitters and phenylalanine in the body. It is a rare disorder.
A deficiency in Quinoid Dihydropteridine Reductase
can also cause immune suppression in pancreatic cancer.
|
| R |
| RAD51C, RAD51D
genes
are
essential for DNA repair. Pathogenic
germline mutations in these genes are linked to breast and gynecologic cancers (cervical, ovarian, uterine). |
| RB1
is a tumor suppressor gene. RB1
was the first tumor suppressor gene discovered. Pathogenic
germline mutations in RB1 can cause Retinoblastoma, a childhood cancer of the retina. |
| RINT1 gene encodes RAD50-interacting protein 1. It is a tumor suppressor gene. Germline mutations in RINT1
have been associated with an increased risk breast cancer and Lynch
syndrome. |
| RNA
or
ribonucleic acid, is a single-stranded nucleic acid that carries out the genetic instructions encoded in
DNA. There are several different types,
including Messenger RNA (mRNA), Ribosomal RNA
(rRNA), Transfer RNA (tRNA). Each has a specific function.
RNA's role in
cancer development, treatment, and prevention are just starting
to be explored.
|
| S |
|
SDHA
genes provide the instructions for making one part of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) enzyme. This enzyme plays an important role helping convert food into a form of energy that cells can use.
Pathogenic germline
mutations in SDHA genes are linked to gastrointestinal and endocrine tumors and cancers. |
| Sharing
Genetic information
|
|
Somatic Mutations
are genetic changes that happen occur after conception to
some of the cells in your body. Your cells are constantly dividing. They divide to help children grow and to replace old, damaged, or dead cells in adults. As cells divide, mistakes can happen as genes are being copied from one cell to the next. Most somatic mutations cause no harm. However, occasionally, genetic errors can accumulate as you age and cause cancer or other diseases.
|
|
STK11 genes are a tumor suppressor genes that helps regulate cell growth and programmed cell death.
Pathogenic germline
mutations in the STK11 genes are the cause most cases of
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome.
|
| T
|
|
TP53 is a tumor suppressor gene. It is the most frequently mutated gene found in cancer.
Pathogenic germline
TP53 mutations are linked to breast, colorectal, and other cancers. It is also associated with
Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
|
|
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC)
is a type of breast cancer with no estrogen, progesterone, or HER2 receptors on the tumor. TNBC
is usually more aggressive, with a faster growth rate and a higher risk of metastasis and recurrence.
TNBC can be a red flag for hereditary cancer.
|
|
Tumor Suppressor Genes are genes that play important roles in regulating cell growth, cell proliferation, DNA repair, and programmed cell death
(apoptosis.) If tumor suppressor genes don't function properly because of a mutation, cells can grow out of control and lead to cancer.
|
|
TSC1 & TSC2
are protein encoding genes that help regulate cell growth and division. Pathogenic germline mutations in these genes are associated with endocrine, gastrointestinal, renal/urinary tract, and nervous system/brain cancers.
|
| U |
|
Unknown Primary or Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP) is when it is uncertain which organ or tissue a cancer originally came from. CUP can be associated with inherited cancer syndromes. |
UGT1A1
is a gene that codes for an enzyme involved in normal liver metabolism. A normal variation (a polymorphism) of the UGT1A1 gene called UGT1A1*28 is associated with a hereditary syndrome called Gilbert's Syndrome which affects about 10% of the population. Gilbert syndrome is a benign condition that causes the liver to have problems removing bilirubin from the blood.
However, with a UGT1A1 polymorphism, you may metabolize specific chemotherapy drugs differently - namely
Irinotecan which is commonly used in colorectal cancer - causing more of the drug to build up in your system which causes more drug side effects. Before taking
Irinotecan or other drugs in this class, you should be screened for UGT1A1 polymorphism. |
| V |
| Variant
-- in genetics,
is a permanent alteration in a gene's DNA makeup. See mutation. |
| Variant of
Uncertain Significance (VUS) is a change in a gene, but it is unknown whether that variant is actually connected to any health condition, such as cancer. Determining whether or not a VUS is disease-causing can be
a lengthy process that relies on multiple sources of collected evidence. |
| VHL
gene, is a tumor suppressor gene. Germline pathogenic
mutations in VHL genes are linked to specific types of cysts,
tumors--both benign and malignant--in several organ systems. |
| W |
| Werner's Syndrome
affects children/young adults and predisposes them to cancer due to an inherited mutation in the WRN gene which may cause errors in DNA to accumulate.
Werner's Syndrome is an autosomal recessive syndrome, which means a mutated gene from both parents must be
passed on for a child to be affected. |
| WRN Genes
are DNA repair genes. WRN genes provide instructions for producing the Werner protein, which is critical for repairing damaged DNA. |
| WT1
or Wilms' Tumor Suppressor Gene 1 has an essential role in healthy urinary, kidney, and blood cell development.
Pathogenic germline WT1 gene mutations are associated with a number of malignancies. |
| X |
| X
chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes found in many organisms, including humans. It is found in both males and females. The other sex chromosome is
Y. These two special chromosomes, along with many other genes in our genome, determine our sex. Generally, females have a pair of X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. |
| Xeroderma Pigmentosum
are is an inherited syndrome predisposing individual to skin cancer, including melanoma, caused by mutation in the XP gene. XP genes are involved in repairing DNA. Xeroderma Pigmentosum is an autosomal recessive
syndrome, which means a mutated gene from both parents must be
passed on for a child to be affected. |
| Y |
Y
chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes found in many organisms, including humans. It is commonly associated with males, but the Y chromosome does not singularly determine a person's gender. The other sex chromosome is
X.
It is not uncommon to for people to be born with an extra copy of a chromosome, (YXX, YYX, XXX) or to lose a Y chromosome as they age.) |
| Z
|
| Z-DNA
is one of the many structures of DNA. It is the "lefthanded" form. That means its double helix winds to the left in a zigzag pattern instead of to the right like the more common B-DNA form.
|
|
|
|
Knowing and
sharing your family's health and cancer history with your health
care providers and your family
(children, parents, siblings, aunts, uncles, nieces,
nephews, and first and second cousins) can be life-saving.

Download the
Fillable Pedigree PDF
Some
red flags of hereditary cancer:
 Breast, colorectal, or uterine cancers under the age of 50.
Breast, colorectal, or uterine cancers under the age of 50.
 Triple-negative breast cancer.
(Breast cancer with no estrogen, progesterone, or HER2 receptors on the
tumor.)
Triple-negative breast cancer.
(Breast cancer with no estrogen, progesterone, or HER2 receptors on the
tumor.)
 Male breast cancer diagnosed at any age.
Male breast cancer diagnosed at any age.
 Two separate cancer diagnoses in the same family member.
Example: Both pancreatic and breast cancers in one individual.
Two separate cancer diagnoses in the same family member.
Example: Both pancreatic and breast cancers in one individual.
 Ovarian cancer at any age, especially in younger women.
Ovarian cancer at any age, especially in younger women.
 A known BRCA , Lynch syndrome, or other pathogenic hereditary cancer-related mutation in the family.
And that can be in a close genetic relative or one separated by many degrees.
A known BRCA , Lynch syndrome, or other pathogenic hereditary cancer-related mutation in the family.
And that can be in a close genetic relative or one separated by many degrees.
 Being of Ashkenazi Jewish descent with a history of cancer at any age.
Being of Ashkenazi Jewish descent with a history of cancer at any age.
 Multiple family members with the same type of cancer or related cancers
(like breast, ovarian, pancreatic, or prostate).
Multiple family members with the same type of cancer or related cancers
(like breast, ovarian, pancreatic, or prostate).
 Pancreatic cancer at any age.
Pancreatic cancer at any age.
 Metastatic prostate cancer.
Metastatic prostate cancer.
|
|
|
If
you need
genetic counseling and testing because of family cancer history, or
if you have been
diagnosed with a pathogenic germline mutation or hereditary cancer,
the nonprofit organizations listed below are here to
help: |
|
|
NSGC
Find a genetic counselor at the National Society of Genetic Counselors.
|
|

Connect
My Variant
Prevention through connection. ConnectMyVariant is an educational health-focused nonprofit organization that supports individuals and families with hereditary disease, such as cancer risk, in their early detection and prevention efforts.
The mission of ConnectMyVariant.org is “to end hereditary disease by bringing families
together.”
|
|

My Faulty Gene is a nonprofit organization which provides information and assistance to underrepresented, uninsured, and underinsured individuals whose family medical history suggests genetic testing might be helpful in identifying an increased risk of disease due to a genetic mutation.
Genetic testing saves lives!
|
|

Testimonials from individuals affected by hereditary cancers.

|
|
Jacqueline
Rush Foundation
Helping to save lives by improving public and medical community awareness of Lynch Syndrome and to raise funds for Lynch Syndrome research.
|
|
Alive and Kick'n
To improve the lives of individuals and families affected by
Lynch syndrome and associated cancers through research,
education and screening |
|

Lynch Syndrome Awareness
Spreading Awareness and Education about Lynch Syndrome. Empowering individuals with knowledge and resources to understand and combat Lynch Syndrome effectively.
|
|

No Stomach For Cancer (NSFC)
helps you recognize
the signs and symptoms of stomach cancer, and understand the
risk factors and preventative efforts you can make. Here you can find answers to questions about stomach cancer treatments, including gastrectomy, and ways to help improve the quality of your life without a stomach. NSFC is a network of
caring.
Learn more about Jewell’s Rules, a free
Patient and Caregiver Guide for Pediatric Gastric
Concerns.

|
|
BRCAStrong
offers education, information, support and advocacy for women who are uninsured or under insured, by women who care. Support comes in all forms , from premastectomy care packages, gynecological care packages, post-mastectomy garments, prosthetics and other treatment necessities; and is provided at zero cost to recipients. |
|
26.2 Step Mini Marathon
is a one-of-a-kind event. It brings the fun of a mini marathon together with the goal to raise awareness of high-risk cancers; to empower people to make a health care plan; and to help them take those next action "steps". |
|
FORCE-Facing Our Risk of Cancer Empowered
Helping to improve the lives of individuals and families facing hereditary cancer.
|
|
From the
creator of this site:

Learn more. Click
here.
|
|

|
| In this book you will find fun art activities that highlight some incredibly fascinating facts about DNA, and why it helps make you you.
And you’ll also learn how your DNA connects you to all life on Earth.
Free
PDF download |
|
|
|
|
|
|
![]()